認知神經科學的應用
Applications of Cognitive Neuroscience
高精度感測元件
High-resolution Sensors and Devices
High-resolution Sensors and Devices
機器學習於腦科學應用
Application of Machine Learning in
Brain Research
Application of Machine Learning in
Brain Research
認知神經科學的應用
Applications of Cognitive Neuroscience
Applications of Cognitive Neuroscience
疲勞偵測系統
An EEG-based Fatigue Detection and Mitigation System
An EEG-based Fatigue Detection and Mitigation System
腦中心研究深入探討疲勞引起的神經訊號變化特徵,通過即時的腦電波(EEG)偵測,並展示了透過即時的腦電波偵測開發的線上閉迴路疲勞偵測以及緩減系統,從而可以防止疲勞所致認知行為低下可能造成的致命傷害。
Our research explores neurophysiological changes, measured by electroencephalogram (EEG), due to fatigue. In addition, we further demonstrate the feasibility of an online closed-loop EEG-based fatigue detection and mitigation system that detects physiological change and can thereby prevent fatigue-related cognitive lapses.
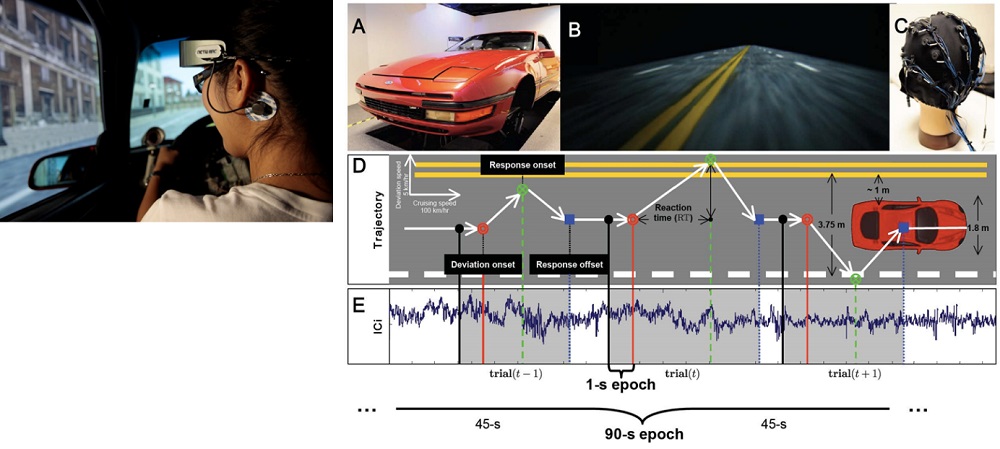
- Lin, C. T., Huang, K. C., Chao, C. F., Chen, J. A., Chiu, T. W., Ko, L. W., & Jung, T. P. (2010). Tonic and phasic EEG and behavioral changes induced by arousing feedback. NeuroImage, 52(2), 633-642.
- Lin, C. T., Huang, K. C., Chuang, C. H., Ko, L. W., & Jung, T. P. (2013). Can arousing feedback rectify lapses in driving? Prediction from EEG power spectra. Journal of neural engineering, 10(5).
- Wang, H., Zhang, C., Shi, T., Wang, F., & Ma, S. (2015). Real-time EEG-based detection of fatigue driving danger for accident prediction. International journal of neural systems, 25(02).
- Huang, K. C., Huang, T. Y., Chuang, C. H., King, J. T., Wang, Y. K., Lin, C. T., & Jung, T. P. (2016). An EEG-based fatigue detection and mitigation system. International journal of neural systems, 26(04).
暈車及多重任務分心駕駛
Motion sickness and distracted driving
Motion sickness and distracted driving
我們研究解譯由使用六軸平台運動引起的模擬暈車狀態時的大腦變化動態,並且採用時間序列的相關分析來評估暈車的程度與大腦變化的關係。此外,我們研究也比較了駕駛和乘客之間暈車程度的問題,用腦動態分析證明乘客需要更多外在感知的神經生理系統的調節過程。
We explored the brain dynamics with motion sickness induced by the motion of the platform. Additionally, time series cross-correlation analysis was employed to evaluate relationships between the spectral changes associated with different brain processes and the degree of motion sickness.
Furthermore, our research revealed brain dynamics in motion sickness among passengers and drivers to indicate that the passenger experience more conflicts among multimodal sensory systems and demand neuro-physiological regulation.
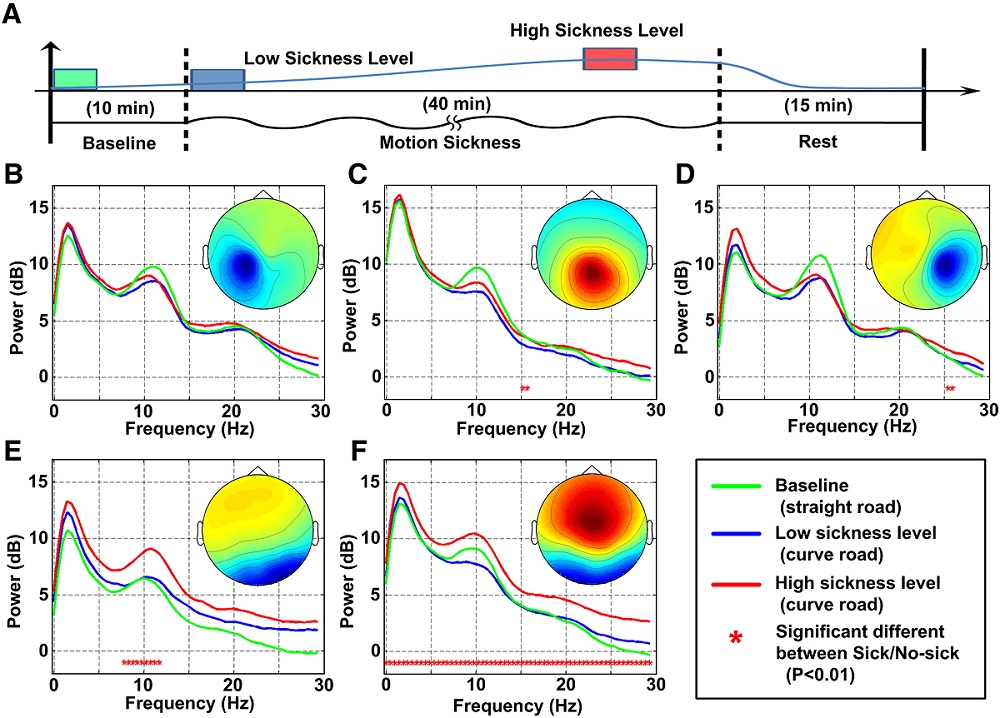
- Chen, Y. C., Duann, J. R., Chuang, S. W., Lin, C. L., Ko, L. W., Jung, T. P., & Lin, C. T. (2010). Spatial and temporal EEG dynamics of motion sickness. NeuroImage, 49(3), 2862-2870.
- Huang, K. C., John, A. R., Jung, T. P., Tsai, W. F., Yu, Y. H., & Lin, C. T. (2021). Comparing the Differences in Brain Activities and Neural Comodulations Associated With Motion Sickness Between Drivers and Passengers. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 29, 1259-1267.
我們也對於駕駛分心時的大腦變化進行研究,並提出了一種基於腦電波的腦機介面系統,利用機器學習技術進行分心的偵測。
We also investigate brain dynamics about distracted driving and propose a BCI system based on EEG for distracted driving with machine learning technologies.
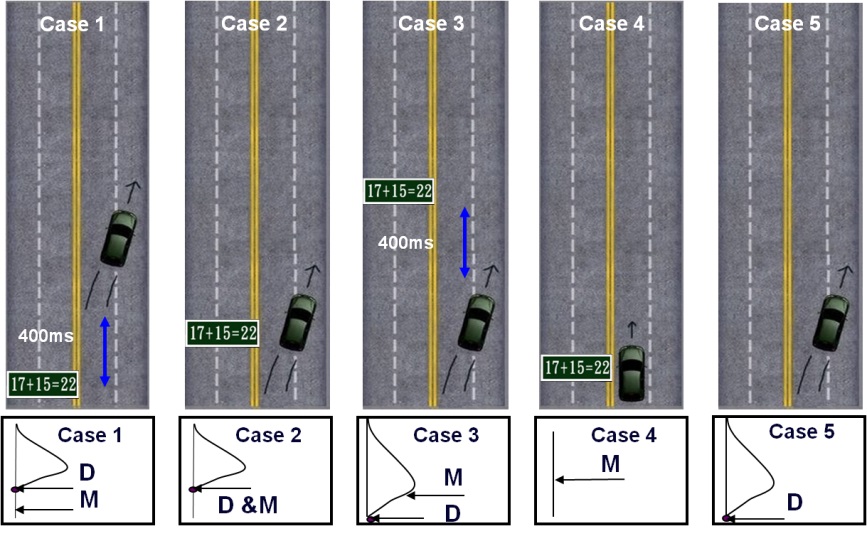
- Lin, C. T., Chen, S. A., Chiu, T. T., Lin, H. Z., & Ko, L. W. (2011). Spatial and temporal EEG dynamics of dual-task driving performance. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation, 8(1), 1-13.
- Wang, Y. K., Chen, S. A., & Lin, C. T. (2014). An EEG-based brain–computer interface for dual task driving detection. Neurocomputing, 129, 85-93.
- Wang, Y. K., Jung, T. P., & Lin, C. T. (2015). EEG-based attention tracking during distracted driving. IEEE transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering, 23(6), 1085-1094.
大腦訊息傳遞連接網路
Brain Connectivity
Brain Connectivity
模擬大腦神經動態與神經訊息傳遞預測認知行為狀態是近年來另一個在神經科學的關鍵研究目標。
駕駛任務中的大腦連接
研究表明駕駛者的感知訊息增加在要求相對更高感知能力的任務,在神經網路中有明顯的傳遞能量。大腦網路動態可對理解駕駛者注意力的變化,對設計駕駛者輔助系統具有重大意義。
To model temporal changes in neural dynamics and information flow that index and predict task-relevant changes in cognitive state and behavior is a critical study in neuroscience.
駕駛任務中的大腦連接
Brain Connectivity in Driving Tasks
研究表明駕駛者的感知訊息增加在要求相對更高感知能力的任務,在神經網路中有明顯的傳遞能量。大腦網路動態可對理解駕駛者注意力的變化,對設計駕駛者輔助系統具有重大意義。
This study showed that the driver’s salient sensory information imposes a relatively more perceptually-demanding task, leading to stronger activation in the task-positive network. The brain network dynamics could have major implications for understanding fluctuations in driver attention and designing advanced driver assistance systems.
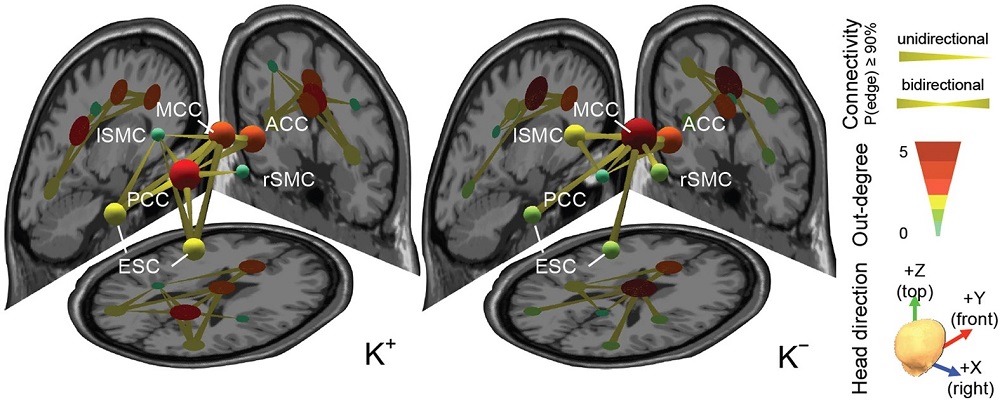
- Lin, C. T., Chuang, C. H., Kerick, S., Mullen, T., Jung, T. P., Ko, L. W., Chen, S. A., King, J. T. & McDowell, K. (2016). Mind-wandering tends to occur under low perceptual demands during driving. Scientific reports, 6(1), 1-11.
- Huang, C. S., Pal, N. R., Chuang, C. H., & Lin, C. T. (2015). Identifying changes in EEG information transfer during drowsy driving by transfer entropy. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 9, 570.
大腦動態調控機制
Modulation of brain dynamics
Modulation of brain dynamics
為了研究生理神經調節系統,我們提出了獨立調控因子分解以評估疲勞、頭暈等情況的大腦協同調節。
To investigate the physiological and neural modulatory system, we proposes independent modulator decomposition to assess co-modulators in the brain during the drowsiness and motion sickness dimension.
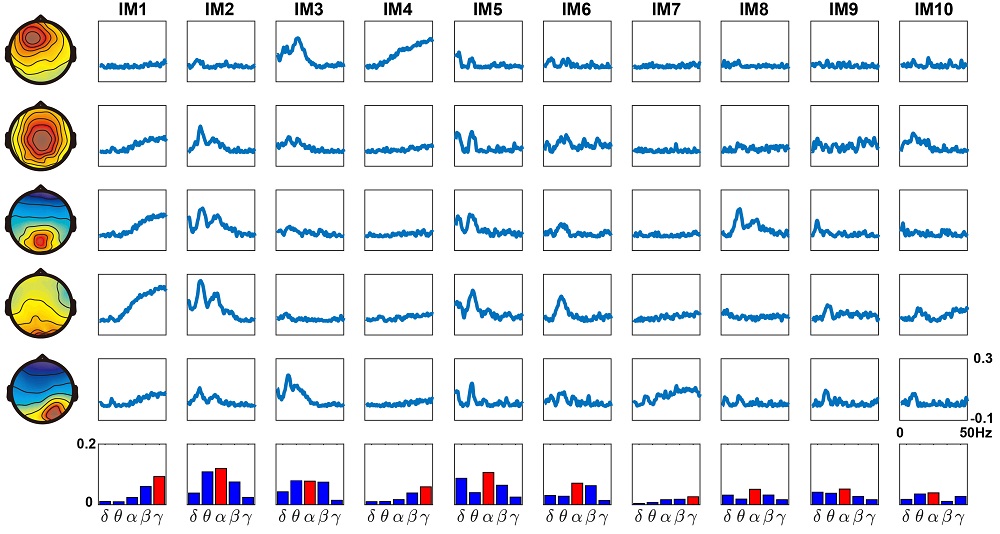
- Chuang, S. W., Ko, L. W., Lin, Y. P., Huang, R. S., Jung, T. P., & Lin, C. T. (2012). Co-modulatory spectral changes in independent brain processes are correlated with task performance. Neuroimage, 62(3), 1469-1477.
- Chuang, S. W., Chuang, C. H., Yu, Y. H., King, J. T., & Lin, C. T. (2016). EEG alpha and gamma modulators mediate motion sickness-related spectral responses. International journal of neural systems, 26(02), 1650007.
- Huang, K. C., John, A. R., Jung, T. P., Tsai, W. F., Yu, Y. H., & Lin, C. T. (2021). Investigating brain activities and neural comodulations in motion sickness between passengers and drivers. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering: a Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society.