認知神經科學的應用
Applications of Cognitive Neuroscience
高精度感測元件
High-resolution Sensors and Devices
High-resolution Sensors and Devices
機器學習於腦科學應用
Application of Machine Learning in
Brain Research
Application of Machine Learning in
Brain Research
機器學習於腦科學應用
Application of Machine Learning in Brain Research
Application of Machine Learning in Brain Research
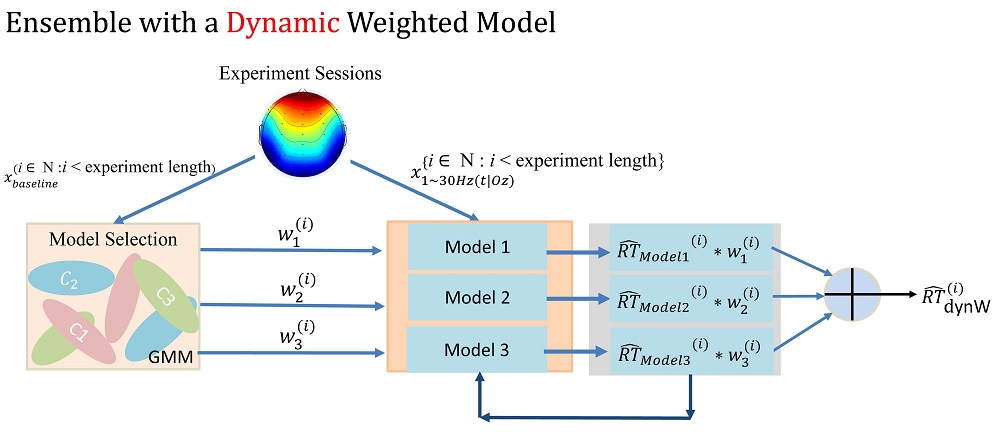
動態權重調整疲勞預測系統
Dynamically Weighted Ensemble-based Fatigue Prediction System
Dynamically Weighted Ensemble-based Fatigue Prediction System
個體之間的差異可能造成人們大腦基準狀態的改變進而影響行為表現以及大腦活動之間的關係,造成難以使用廣義預測模型來預測每種狀態,為此我們建立整合學習動態權重調整疲勞預測系統。
Individuals’ differences may cause changes in the baseline of brains and affect behavioral performance and the relationship between brain activities. It is hard to use generalized prediction models to fit each state. Therefore, we purpose an ensemble-based weighted fatigue prediction system.
大數據 vs. 稀疏數據
Big Data vs. Sparse Data
Big Data vs. Sparse Data
當某些認知特徵類別相對於其他類別的代表性不足時,就會出現機器學習中的類別不平衡問題,從而導致對多數類別的學習偏差。我們提出了一種新的過採樣算法,稱為內核自適應子空間中的少數過採樣(MOKAS),利用了自適應子空間自組織映射的內核不變特徵提取特性。新合成的資料會從已訓練完成的子空間生成,在輸入空間中重建原始特徵資料。
The class imbalance problem in machine learning occurs when certain cognitive feature classes are underrepresented relative to the others, leading to a learning bias toward the majority classes.
To reduce information loss during feature space projection, we proposes a novel oversampling algorithm, named minority oversampling in kernel adaptive subspaces (MOKAS), which exploits the invariant feature extraction capability of a kernel version of the adaptive subspace self-organizing maps. The synthetic instances are generated from well-trained subspaces and then their pre-images are reconstructed in the input space.
- Lin, C. T., Hsieh, T. Y., Liu, Y. T., Lin, Y. Y., Fang, C. N., Wang, Y. K., ... & Chuang, C. H. (2017). Minority oversampling in kernel adaptive subspaces for class imbalanced datasets. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 30(5), 950-962.
深度學習用於認知狀態預測
Deep Learning in cognitive states prediction
Deep Learning in cognitive states prediction
EEG是很有效的觀察大腦認知行為的變化的指標。我們綜合腦電波三維(3-D)的資料,即頻率、時間和通道位置訊息。我們提出了一種4-D卷積神經網路(4-D CNN, 4-D Convolutional Neural Network),加上EEG訊號的腦波和相對應的行為表現的變化做為第四維資訊,經過測試4-D CNN的預測性能優於2-D CNN、3-D CNN和淺層神經網路。而這也有助於增強我們對 EEG 信號分析中深度學習方法的理解。
Tel
Electroencephalography (EEG) has been demonstrated to be effective for monitoring changes in the human brain state and behavior. Three domains, namely, frequency, temporal, and channel spatial information were comprehensively considered. A 4-D convolutional neural-network (4-D CNN) algorithm was then proposed to associate all information from the EEG signals and the changes in the human state and behavioral performance. A 4-D CNN achieves superior forecasting performance over 2-D CNN, 3-D CNN, and shallow networks. This work also contributes to enhancing our understanding of deep learning methods in the analysis of EEG signals.
- Lin, C. T., Chuang, C. H., Hung, Y. C., Fang, C. N., Wu, D., & Wang, Y. K. (2020). A driving performance forecasting system based on brain dynamic state analysis using 4-D convolutional neural networks. IEEE transactions on cybernetics.
解碼使用華語說話的腦動態以建構直述語意的腦機介面
Decoding brain dynamics of speaking Mandarin for building a Direct Speech Brain-Computer Interface
Decoding brain dynamics of speaking Mandarin for building a Direct Speech Brain-Computer Interface
如何解碼人腦中感覺運動皮層活動以解析溝通的言語/語意,一直是神經科學家面臨的巨大挑戰之一。透過擷取在說話時表達語意的腦電波訊號的特徵,建立可直接由控制腦部活動想像說話就能溝通表達的腦機介面;對於一般人使用上,直接以語言/語意解譯,相較於用想像,可提供腦波操作應用更直接精確的指令。然而華語做為世界上相當重要的語言之一,卻沒有針對在使用華語溝通交流時,生理訊號的變化特徵研究。我們提出解碼在使用華語時的非侵入式的腦電波(Electroencephalography, EEG)生理訊號特徵,並結合人工智慧機器學習辨識,建構Direct-Speech Brain-Computer Interface (DS-BCI)以直接從運動和語言相關的腦區域的活動解譯,透過擷取使用華語(普通話)的語意行為時的腦電波訊號進行特徵分析,找出腦動態變化,歸納生理特徵和語意的關連性,並藉由智慧型機器學習的演算方法,來實現基於腦波的華語語音表達的腦機介面。
Decoding of human sensorimotor cortex for speech articulation is the grand challenge for neural scientist. Applying brain-computer interface is a promising strategy to recognize human expressions from the continuous decoding of neural signals underlying speech imagination. For ordinary people, direct interpretation in words/semantics can provide more accurate and intuitive approach instructions for brain operation applications than imagination. However, Mandarin Chinese is one of the popular languages in the world but has few study to explorer the feature brain signals while speaking Mandarin systemically. This project will integrate real-time multi-channel high-density Electroencephalography (EEG) to explore brain dynamics while speaking Mandarin for extracting the speech-related EEG signals feature. Additionally, DS-BCI is proposed by machine learning techniques to achieve a brain-computer interface of Mandarin speech expression.

- Yang, S. R., Jung, T. P., Lin, C. T., Huang, K. C., Wei, C. S., Chiueh, H., Hsin, Y. L., Liou, G. T. & Wang, L. C. (2021). Recognizing Tonal and Non-Tonal Mandarin Sentences for EEG-based Brain-Computer Interface. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems.
探索從輕度認知障礙到失智症病患的生物標記:分析和整合應用系統
Exploring Biomarkers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia subjects: analysis and preliminary integrative system
Exploring Biomarkers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia subjects: analysis and preliminary integrative system
失智症是大眾所熟知與重視的一種老年退化性疾病,尤其近年來失智症(Dementia)的盛行率隨著步入高齡社會有愈來愈高的趨勢,失智症所衍伸的各種治療照顧等相關議題為當前人類社會發展所面臨重大的課題。然而輕度認知障礙到早期失智症的預測被認為有助於預防或延緩失智症的發生。
我們提出探討能做為辨別輕度認知障礙及早期失智症的生物標記,建立預測模型,將使治療更早且有可能更有效。腦電波的生物標記將提供一種非侵入性且相對便宜的篩檢工具,以預測早期失智症的轉化。
我們提出探討能做為辨別輕度認知障礙及早期失智症的生物標記,建立預測模型,將使治療更早且有可能更有效。腦電波的生物標記將提供一種非侵入性且相對便宜的篩檢工具,以預測早期失智症的轉化。
Dementia is a degenerative disease of old age that is well known and valued by the public. In recent years, the prevalence of dementia has become trending as it enters the advanced age society. Related topics such as treatment and care are major issues facing the development of human society. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is considered a transitional stage from a normal cognitive state to the development of dementia. The prediction of MCI and early dementia is considered to help prevent or delay dementia.
We propose the integrative biomarkers to predict MCI and early dementia, and establish a predictive model that enable an earlier, and potentially more effective, treatment of MCI and early dementia. Electroencephalography (EEG) biomarkers would provide a non-invasive and relatively cheap screening tool to predict conversion to early dementia.
We propose the integrative biomarkers to predict MCI and early dementia, and establish a predictive model that enable an earlier, and potentially more effective, treatment of MCI and early dementia. Electroencephalography (EEG) biomarkers would provide a non-invasive and relatively cheap screening tool to predict conversion to early dementia.